One of the frequently used decorators in Python classes, @staticmethod, is utilized to define independent methods logically related to the class. In this article, we will help you understand the features, usage, practical examples of @staticmethod, and compare it with other decorators (@classmethod).
1. What is @staticmethod?
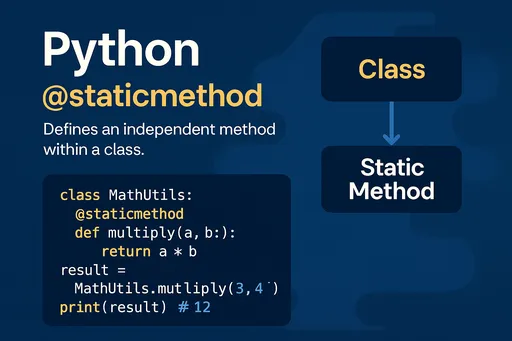
@staticmethod is a decorator used to define independent functions within a class. This method operates without regard to the class's instances or the class itself and does not access the instance (self) or the class (cls).
Main Features - Independent Method: Handles independent logic that does not depend on class or instance attributes. - Logical Grouping: Although it can be defined outside a class, it's cleaner to define it inside if it relates logically to the class. - Calling Method: It can be called through the class name or an instance.
2. When Should You Use @staticmethod?
2.1 Independent Functionality
Use @staticmethod when the class internal method does not need to access instance attributes (self) or class attributes (cls).
class MathUtils:
@staticmethod
def multiply(a, b):
return a * b
result = MathUtils.multiply(3, 4)
print(result) # Output: 12
2.2 Logical Grouping
You can enhance code readability and maintainability by grouping related functions within a class.
class StringUtils:
@staticmethod
def to_uppercase(s):
return s.upper()
print(StringUtils.to_uppercase("hello")) # Output: HELLO
Usage Summary - Independent Functionality: When the method does not need to access properties of an instance or class. - Logical Grouping: When the function is related to the class but does not deal with direct properties.
3. Structure and Usage of @staticmethod
class MyClass:
@staticmethod
def add_numbers(a, b):
return a + b
# Called by class name
result1 = MyClass.add_numbers(3, 5)
print(result1) # Output: 8
# Called by instance
obj = MyClass()
result2 = obj.add_numbers(10, 20)
print(result2) # Output: 30
Feature Analysis - add_numbers provides a simple calculation function that does not depend on class or instance attributes. - It does not use self or cls and is structured as a class-related utility method.
4. Comparison of @staticmethod and @classmethod
| Feature | @staticmethod | @classmethod |
|---|---|---|
| Access to self or cls | No | Access to cls |
| Main Purpose | Define independent utility methods | Define methods dealing with the class state |
| Calling Method | Class name or instance | Class name or instance |
| Usage Example | Simple calculator, formatting functions | Class creation logic, factory methods |
class Example:
class_variable = "I am a class variable"
@staticmethod
def static_method():
return "I am a static method"
@classmethod
def class_method(cls):
return f"I am a class method accessing: {cls.class_variable}"
print(Example.static_method()) # Output: I am a static method
print(Example.class_method()) # Output: I am a class method accessing: I am a class variable
5. Practical Examples of @staticmethod
5.1 Utility Function
class MathUtils:
@staticmethod
def factorial(n):
if n == 0 or n == 1:
return 1
return n * MathUtils.factorial(n - 1)
print(MathUtils.factorial(5)) # Output: 120
5.2 Data Formatting
class StringUtils:
@staticmethod
def to_snake_case(s):
return s.replace(" ", "_").lower()
print(StringUtils.to_snake_case("Hello World")) # Output: hello_world
6. Advantages
- Code Grouping: Enhances readability and maintainability by grouping independent methods related to the class in one place.
- Elimination of Unnecessary Dependencies: Allows writing more concise and clear code in functions that do not require
selforcls. - Logical Organization: Facilitates logical structuring of functions related to the class.
7. Summary
@staticmethod is used to define independent methods that are related to the class but do not depend on instance or class attributes. While it can be defined outside a class, it's preferable to define it inside to maintain logical relationships.
Utilize @staticmethod to enhance the readability and efficiency of your code! 😊


![thumbnail of [Python Standard Library - 5] Working with Numbers: Using math and statistics](/media/editor_temp/6/b61bc8e3-5ac9-46fd-b6e2-129e91d7931b.png)

![thumbnail of [Python Standard Library - 3] Handling Time with Python: datetime](/media/editor_temp/6/5843a4cb-f3a6-4d8d-9a13-89c1cbb0ef6c.png)
There are no comments.